What is PATROL
PATROL is the first procurement of the EU Agency for the Space Programme (EUSPA) that exploits the advantages of Galileo Open Service Navigation Message Authentication (OSNMA) in smart tachographs. The result poses the bases for the adoption of Galileo OSNMA in several other civil applications that need robust navigation.
The PATROL (Position Authenticated Tachograph foR OSNMA Launch) project has the objective to develop a User Terminal providing trusted Position Navigation and Time (PNT) for smart tachographs. PATROL uses the satellite navigation signals coming from Galileo and GPS, and moreover leverages the authentication feature of the Galileo Open Service Navigation Message Authentication (OSNMA).
The project has been awarded by the EU Agency for the Space Programme (EUSPA) and the team is composed by Qascom, FDC, ST Microelectronics, GMV aerospace and Defence, Actia and the University of Padova.
Objectives
The main objective is to deliver a robust PNT (Position, Navigation, Time) solution, embodied in an User Terminal and compliant to the new smart tachographs regulations.
On the receiver side, OSNMA is complemented by additional GNSS spoofing detection techniques and IT security features, in order to meet the smart tachograph requirements and ensure a robust PNT.
The developed solution is validated against a full set of possible threat scenarios.
The project objectives are to:
Develop the first GNSS User Terminal with Galileo OS Navigation Message Authentication (OSNMA) for smart tachographs, using commercial GNSS receivers.
Develop a European GNSS validation platform to test GNSS receivers against emerging threats.
Assess GNSS vulnerabilities, with and without OSNMA service.
Implement state of the art GNSS threat mitigation strategies, complementary to OSNMA.
Facilitate the adoption of OSNMA in the tachograph industry and other markets.
PATROL Conceptual mode
Main results
The project delivers the hardware/software components of the:
User Terminal (UT).
Validation Platform (VP).
Additionally, the project produces draft guidelines for the implementation of OSNMA in receivers, obtained from an extensive performance assessment campaign.
The user terminal
The User Terminal (UT) is a product, compliant with the new Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) 2018/502 of 28 February 2018, for the provision of trusted position and time using satellite navigation systems.
From a high-level perspective, the User Terminal is able to:
Process the OSNMA signal and data.
Accept OSNMA keys from external source.
Implement effective Spoofing Detection and Mitigation techniques.
Generate log to allow the performances’ analysis.
Interface with smart tachographs to provide a trusted PVT.
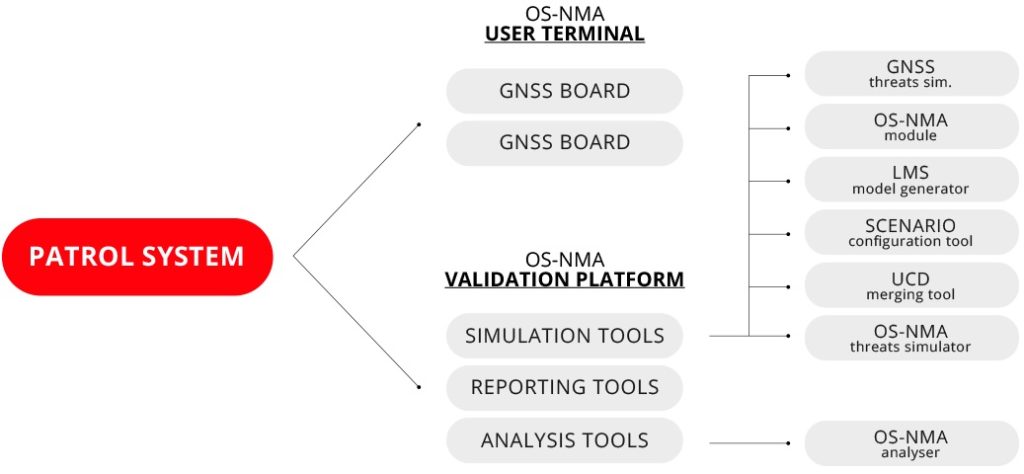
The following image illustrates the block diagram of the User Terminal
User terminal subsystems
The User Terminal includes a dual-frequency L1 and L5 Galileo and GPS board, a module for the use of Galileo OSNMA, Sensor Fusion, a Centralized Authentication Management (CAM) software, tamper detection technologies, advanced GNSS spoofing mitigation techniques. The User Terminal features are complemented with a set of tools able to emulate a Smart Tachograph, provide CAN BUS interface, generate synthetic CAN data for simulation purposes and interface to the GNSS Board for configuration and loading of the OSNMA keys.
The following image illustrates the first version of the PATROL User Terminal.

Patrol user terminal
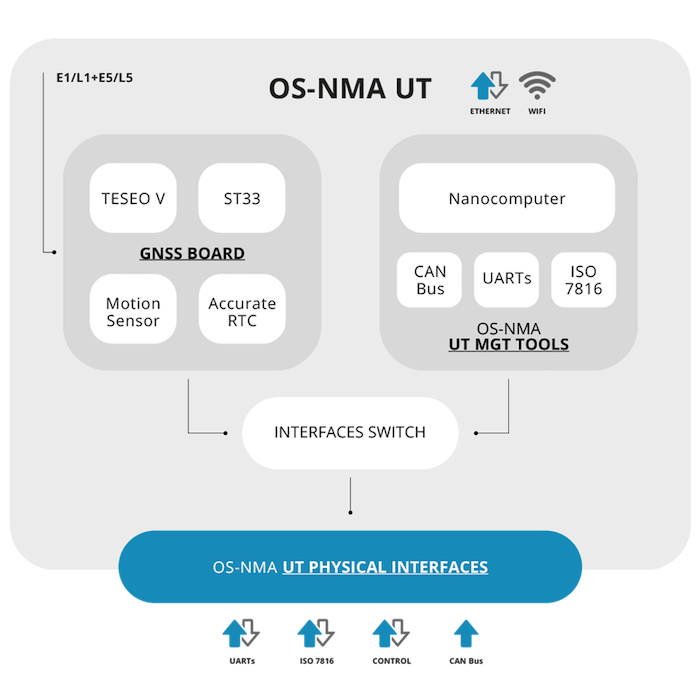
Extended EGF
The User Terminal can be seen as an External GNSS Facility (EGF) of smart tachographs. With respect to the baseline EGF, the UT shows:
A set of debug interfaces, to log various information and control the board.
An external interface to in-vehicle sensors.
A Central Authentication Management software.
An accurate Real Time Clock that could serve as a backup time source when GNSS is not available.
The following image illustrates the default EGF blocks are in white and the novel blocks introduced by the UT in green.
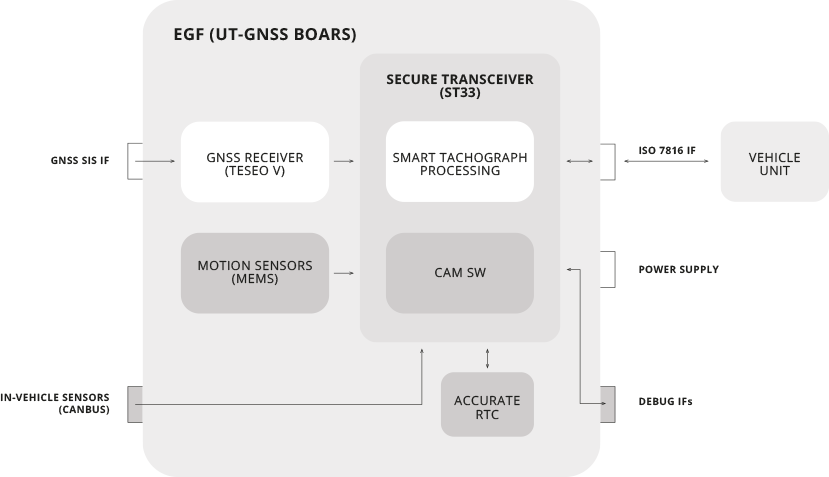
Extended EGF concept
Interface
The User Terminal is controlled by a web interface which allows to:
Setup GNSS board configuration.
Configure anti-spoofing algorithms (CAM software).
Display and log trusted GNSS board information.
Simulate vehicle CAN bus data (for demonstration purpose).
Simulate Digital Tachograph VU (Vehicle Unit) interface and protocol.
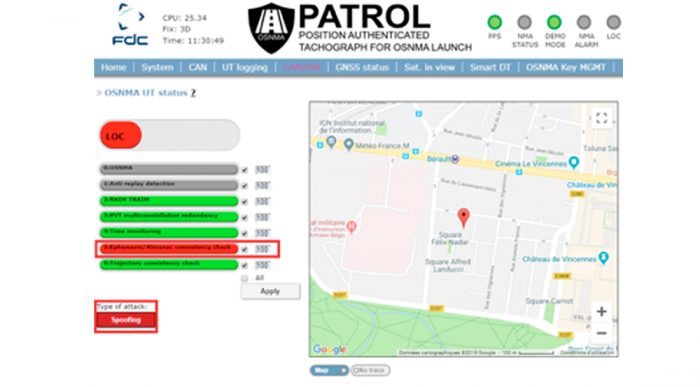
PATROL User Terminal Web interface
Additional interference mitigation technologies
To complement OSNMA, a number of leading-edge and innovative anti-spoofing mechanisms are implemented in the User Terminal, including:
Chipset based anti-spoofing: AGC monitoring, CN0 monitoring, Signal Quality monitoring, Code-carrier consistency checking, OSNMA implementation, unpredictability-based SCER detection, Machine Learning Anti-spoofing, SBAS Data Checks, RAIM and Time RAIM, Position and Time Multi-constellation Redundancy Check
Application based anti-spoofing: Time Monitoring, Ephemeris monitoring, Almanac monitoring, Tracked satellites monitoring, TTFF monitoring, Integration with external sensors (odometer, accelerometer, gyrometer)
The following image illustrates the anti-spoofing techniques proposed in PATROL.
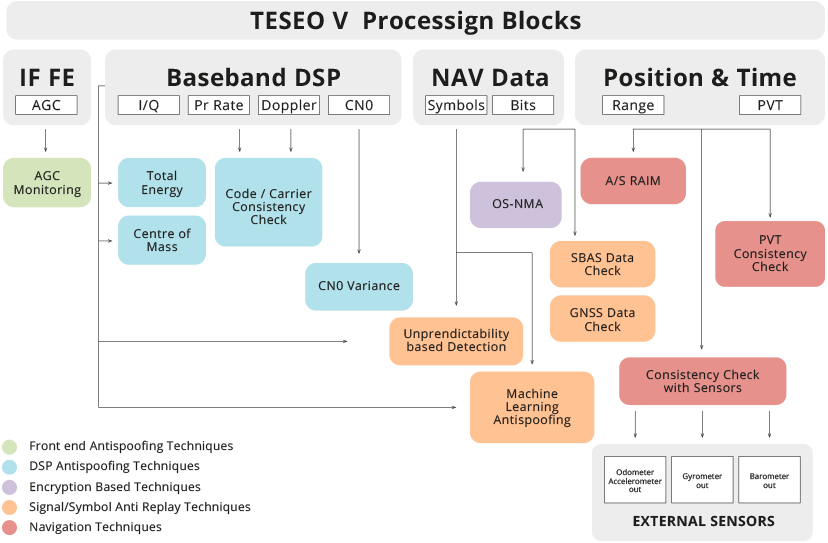
High level diagram of anti-spoofing techniques integrated in the GNSS receiver
The validation platform
- The Validation Platform (VP) allows the end-to-end testing of the user terminal, supporting simulation of GNSS signals and advanced spoofing attacks, generation of OSNMA data, modelling of user environments. It is installed in the Joint Research Centre of the European Commission in ISPRA, and leverages some of the tools already existing there. The Validation Platform allows to measures the User Terminal performances against a number of key performance indicators. In future, it can be enhanced for the test campaign of several applications that need to validate Galileo Open Service Authentication. The Validation Platform enables both simulated and real-field environments, and provides automated tools for the generation of test results. It is composed by the following sub-systems:
- The Simulation Tool is in charge of creating scenarios and generating the RF signal. It comprises:
- The Scenario Configuration Tool (SCT) is a software application that guides the system operator in the configuration of the validation platform scenario.
- The Threat Simulator (TS, furnished by EUSPA) is a software that interfaces with the RFCS for the simulation of GNSS spoofing attacks.
- The UCD merging tool (MRG) allows merging of UCD files containing the LMS and the TS commands. The tools allow to have both LMS and spoofing attacks in the RFCS scenario.
- The Channel Model Generator (LMS) is a software tool being able to generate a timeseries of command for the simulation of the LMS model in the RFCS. The use of LMS model increases realism of OSNMA data reception performances in the simulated environments.
- OSNMA Data Generator (NMA, furnished by EUSPA) module generates the OSNMA data. It generates a I/NAV file containing NMA data to be used in the RFCS simulation.
- The GNSS Signal Simulator (RFCS, furnished by EUSPA) is responsible for the RF generation of the GNSS signal in simulated environment. It’s a Spirent GSS9000 constellation simulator.
- The OSNMA Threat Simulator software (OTS) is a software defined GNSS signal generator being able to simulate a specific subset of advanced GNSS threats (e.g. SCER attack).
- The Record & Replay device (RRP) used to play back the signal samples generated by the OTS.
- The Analysis Tool is in charge of generating test results information on the basis of the information logged by the User Terminal and other entities of PATROL system (RFCS, NMA module, reference trajectories, etc.). It includes:
- KPG: KPIs GEN for the computation of the KPIs • ONA: OSNMA Analyzer for the computation of references OS-NMA results.
- The Reporting Tool converts the output of the Analysis Tools in a human readable format (e.g. tables, figures). The test reports represent the main outcome of the system used to assess the correct OSNMA implementation and performance of the OSNMA User Terminal (UT). This tool enables the qualification of the UT’s resilience against a set of known threats.
- The Validation Platform is designed to stress the capabilities of the User Terminal under different real and simulated conditions. The platform allows to conduct the following activities:
- Test the implementation of the OSNMA algorithm with different configurations.
- Assess the target performances achieved in different reception conditions.
- Assess the robustness level of the OSNMA algorithm against a full set of attacks under a number of operative conditions.
- Determine complementary GNSS measures to be implemented to achieve the best possible level of confidence of the PVT solution.
- The following image illustrates the high level architecture of the Validation Platform.
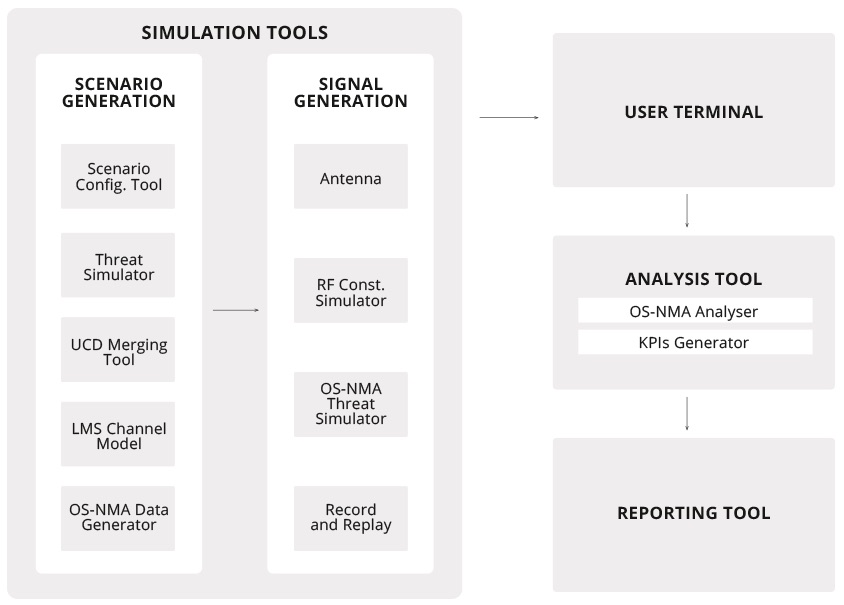
System integration architecture.
Status of the project
The contract has been kicked off in January 2018 and is divided in two subsequent Contract Stages (CS1 and CS2). The CS1 was succesully completed in May 2019. The CS2 has been kicked off in September 2019. The experimentation phase of User Terminal V2 is completed and the CS2 is expected to be concluded in December 2021. The following tests scenarios have been performed:
Test in nominal case, without any threat to the GNSS signal
Test under spoofing, with different type of spoofing signals
OSNMA threats case, investigating especially SCER attacks.
The test campaign of CS1 was performed in representative simulated environment (open sky, suburban and urban channel models). The preliminary analysis on test outcomes highlighted the flexibility, solidity and maturity of the implemented solution. The CS2 focused on testing in real environment, supporting the programme’s OSNMA SIS testing phase. During CS2, PATROL successfully delivered the first close-to-market OSNMA implementation tested with the live signal.
Patrol team
European experts together to develop innovation






